Strona główna Blog Zrozumienie kosztów maszyn do cięcia laserowego: kompleksowy przewodnik
Maszyny do cięcia laserowego stały się niezbędnymi narzędziami w różnych branżach, od produkcji po sztukę i rzemiosło. Ich precyzja, szybkość i wszechstronność sprawiają, że są one preferowanym wyborem do cięcia szerokiej gamy materiałów, w tym metalu, drewna, tworzywa sztucznego i innych. Jednak jednym z najbardziej krytycznych czynników, które przedsiębiorstwa i osoby indywidualne biorą pod uwagę przed inwestycją w maszynę do cięcia laserowego, jest koszt. Ten artykuł zagłębia się w różne aspekty, które wpływają na koszt maszyn do cięcia laserowego, pomagając podjąć świadomą decyzję.
1. Rodzaje maszyn do cięcia laserowego
Koszt maszyny do cięcia laserowego w dużej mierze zależy od jej rodzaju. Istnieją trzy podstawowe typy maszyn do cięcia laserowego:
– Maszyny do cięcia laserowego CO2: Są to najbardziej popularne i wszechstronne typy, odpowiednie do cięcia, grawerowania i znakowania różnych materiałów. Są one ogólnie bardziej przystępne niż inne rodzaje, ale mogą mieć wyższe koszty konserwacji ze względu na konieczność regularnego uzupełniania gazu.
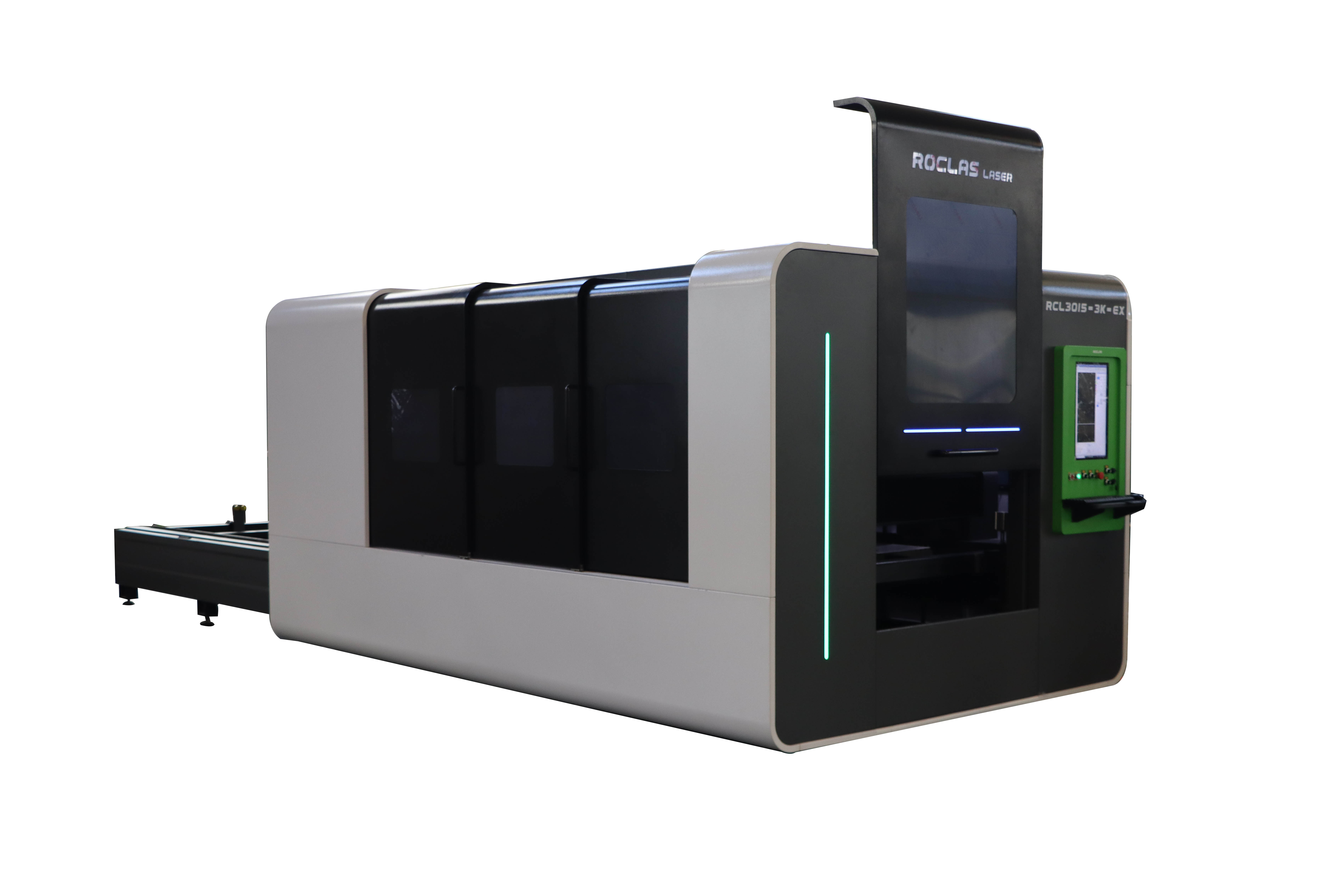
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: Known for their efficiency and precision, fiber lasers are particularly effective for cutting metals. They are more expensive than CO2 lasers but offer lower operating costs and longer lifespans.
- Nd:YAG/Nd:YVO4 Laser Cutting Machines: These are specialized machines used for high-precision applications, such as in the medical and aerospace industries. They are the most expensive type due to their advanced technology and specialized use cases.
2. Power and Performance

The power of the laser, measured in watts, is a significant factor in determining the cost of a laser cutting machine. Higher wattage machines can cut through thicker and more robust materials, but they also come with a higher price tag. For instance, a 100W CO2 laser cutter may cost around $5,000, while a 150W model could be upwards of $10,000. Fiber lasers, which are more efficient, may start at around $20,000 for a 1kW machine and can go up to $100,000 or more for industrial-grade models.
3. Machine Size and Work Area

The size of the laser cutting machine and its work area also impact the cost. Larger machines with bigger work areas are more expensive because they require more materials and advanced engineering to ensure stability and precision. For example, a desktop laser cutter with a small work area might cost around $3,000, while a large-format industrial machine could cost $50,000 or more.
4. Brand and Manufacturer
The brand and manufacturer of the laser cutting machine play a crucial role in its cost. Well-known brands with a reputation for quality and reliability, such as Trumpf, Amada, and Bystronic, often charge a premium for their machines. On the other hand, lesser-known brands or Chinese manufacturers may offer more affordable options, but the quality and after-sales support can vary significantly.
5. Additional Features and Accessories
Laser cutting machines come with a range of additional features and accessories that can influence the overall cost. Some of these include:
- Automatic Focus: This feature adjusts the laser focus automatically, ensuring consistent cutting quality. It adds to the cost but can significantly improve efficiency.
- Rotary Attachment: A rotary attachment allows for the cutting and engraving of cylindrical objects, such as bottles and tubes. This accessory can add several thousand dollars to the machine's price.
- Cooling System: High-powered lasers generate a lot of heat and require an efficient cooling system. Water-cooled systems are more expensive than air-cooled ones but are essential for maintaining the machine's performance and longevity.
- Software: The software that controls the laser cutter can also affect the cost. Advanced software with more features and better user interfaces tends to be more expensive but can enhance the machine's capabilities and ease of use.
6. Operating Costs
While the initial purchase price is a significant consideration, it's also essential to factor in the operating costs of a laser cutting machine. These include:
- Energy Consumption: Higher-powered machines consume more electricity, leading to higher energy bills. Fiber lasers are generally more energy-efficient than CO2 lasers, which can offset their higher initial cost over time.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping a laser cutter in optimal condition. This includes replacing laser tubes, mirrors, lenses, and other consumables. CO2 lasers, in particular, require more frequent maintenance, which can add to the overall cost.
- Gas and Consumables: CO2 lasers require a constant supply of gas (usually CO2, nitrogen, or helium) to operate, which can be a recurring expense. Fiber lasers, on the other hand, do not require gas, reducing their operating costs.
7. Market Trends and Demand
The cost of laser cutting machines can also be influenced by market trends and demand. For example, the increasing adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies has led to a surge in demand for advanced laser cutting machines, driving up prices. Conversely, economic downturns or increased competition among manufacturers can lead to lower prices.
8. Used vs. New Machines
Another factor to consider is whether to purchase a new or used laser cutting machine. Used machines can be significantly cheaper, but they may come with hidden costs, such as the need for repairs or upgrades. It's essential to thoroughly inspect a used machine and consider its remaining lifespan before making a purchase.
9. Financing and Leasing Options
For businesses that cannot afford the upfront cost of a laser cutting machine, financing and leasing options are available. These can spread the cost over several years, making it more manageable. However, it's important to consider the interest rates and terms of the financing agreement, as they can add to the overall cost.
10. Return on Investment (ROI)
Finally, when considering the cost of a laser cutting machine, it's crucial to evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI). A more expensive machine with higher capabilities may lead to increased productivity, reduced material waste, and the ability to take on more complex projects, ultimately generating more revenue. It's essential to weigh the initial cost against the potential long-term benefits.
Conclusion
The cost of a laser cutting machine is influenced by a multitude of factors, including the type of laser, power, size, brand, additional features, operating costs, market trends, and whether the machine is new or used. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and business needs. While the initial investment may be significant, the precision, efficiency, and versatility of laser cutting machines can offer substantial long-term benefits, making them a valuable asset for any business involved in cutting and engraving.
Niezależnie od tego, czy potrzebujesz ogólnej porady czy konkretnego wsparcia, chętnie Ci pomożemy.